
Posts Tagged: Pamela Ronald
Public invited to food security symposium June 4
A public symposium on "Food for a Healthy World: Monitoring progress toward food security" will be held Thursday, June 4, 8:30 a.m. to 12 noon, at the UC Davis Student Community Center. The event is hosted by the UC ANR Agricultural Issues Center and UC Davis World Food Center.
“This program will be of much interest to students, faculty and researchers with an interest in agricultural, environmental and development issues related to sustainable nutrition security,” said Dan Sumner, director of the Agricultural Issues Center.
Discussions will include
- Environmental Quality and Ecosystem Services by William Clark, Harvard University, and Pamela Ronald, UC Davis
- Agricultural Production Issues by Paul West, University of Minnesota, and Jan Hopmans, UC Davis
- Nutrition Security by Barbara Schneeman, US Agency for International Development (USAID), and Bruce German, UC Davis
- Food Policy and Trade by Joseph Glauber, International Food Policy Research Institute, Jikun Huang, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Sumner
The closing discussion will be moderated by Roger Beachy, executive director of the UC Davis World Food Center.
Admission is free. Please RSVP by sending an email to worldfoodcenter@ucdavis.edu. For more information, visit http://aic.ucdavis.edu/events/FoodForHealthyWorld.html or call (530) 752-7172.
GMOs featured in a healthy debate at Berkeley

The class' co-instructor, food writer and activist Michael Pollen, said he is still opposed to the use of GMOs in agriculture, but admitted it's getting lonely in his camp. He said he believes GMOs are tending to more firmly establish mono-cropping practices, favor large-scale industrial agriculture and that Roundup resistant crops are leading to the development of Roundup resistant weeds.
"It's a shame to demonize an entire technology because of Roundup Ready,” Ronald said.
In the New Yorker article, Little shared several of Ronald's points:
- Bt cotton has cut the amount of chemical insecticides applied to crops globally by millions of pounds a year
- Papayas genetically engineered to resist ring-spot virus helped to save the Hawaiian papaya industry
- “Scuba rice,” a strain of flood-tolerant rice that can grow in submerged fields, is being grown by four million subsistence farmers in Bangladesh and India
- The world is filling with ever more people and we need ever more food from the same amount of land
- Genetic engineering will play a critical role in protecting finite soil and water resources, staving off crop diseases, and responding to the pressures of climate change.
Science provides facts for Hawaii GMO debate

The story describes a lone councilman's effort to get science-based information in face of vocal opposition to GMOs among advocacy groups. The lack of input from farmers and scientists on policy issues that affect food and farming has rankled many agircultural scientists, including Pamela Ronald, professor in the Department of Plant Pathology at UC Davis. She compared some advocacy groups' resolute objections to GMOs to people who don't believe the world climate is changing despite the scientific proof.
“Just as many on the political right discount the broad scientific consensus that human activities contribute to global warming, many progressive advocacy groups disregard, reject or ignore the decades of scientific studies demonstrating the safety and wide-reaching benefits” of genetically engineered crops, Ronald said.
Hawaii has a unique status in the GMO debate. It's the only American state where farmers grow genetically modified fruit. After an outbreak of papaya ringspot virus in the mid-1990s, scientists used biotechnology to insert a gene from the virus itself into the papaya that gave it immunity and saved the crop.
The article outlines research showing that many of the claims made by GMO opponents do not stand up to scrutiny. Experts conceded that the research doesn't prove genetically engineered food could never cause harm, but the risks of such crops could be reliably tested, and they had so far proved safe.
“With scientists, we never say anything is 100 percent certain one way or another,” USDA-ARS research molecular biologist Jon Suzuki said. “We weigh conclusions on accumulated knowledge or evidence — but often this is not satisfactory for some.”
The GMO ban was approved by Hawaii's County Council by a 6 to 3 vote and on Dec. 5 signed by the Big Island's mayor.
Would Rachel Carson embrace GMOs?
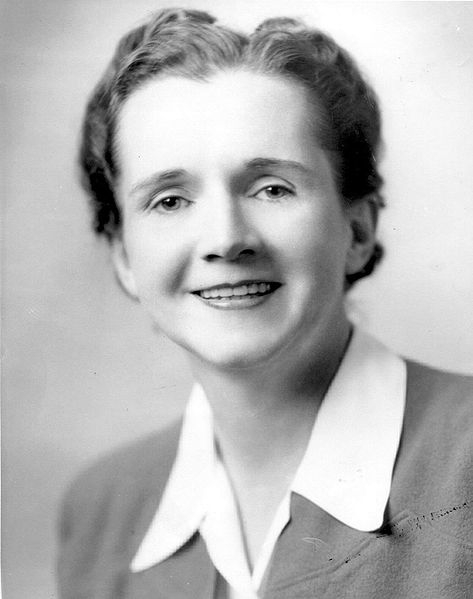
Carson envisioned harnessing the knowledge of biological diversity — entomology, pathology, genetics, physiology, biochemistry and ecology — to shape a new science of biotic controls that would help control weeds, diseases and pests without further damaging the environment, Ronald wrote.
"Her dream of a science-based agricultural system may come as a surprise to those who believe that sustainability and technology are incompatible," the article says.
In her UC Davis laboratory, Ronald has genetically engineered rice that tolerates flooding and resists disease.
"I have to believe that, if Rachel Carson were alive today, she would reject the anti-science, fear-mongering of anti-GE campaigners," Ronald said.
We All Have It: Innate Immunity
What do flies have in common with us? For one thing, an innate immune system mechanism to detect and fight off invaders that threaten our health. Four scientists, including two Nobel Laureates, will discuss host defense at a UC Davis symposium on Wednesday, Jan. 25 in the UC Davis Conference...

Immune system of the tiny Drosophila plays a big role in host defense. (Photo by Kathy Keatley Garvey)
